Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
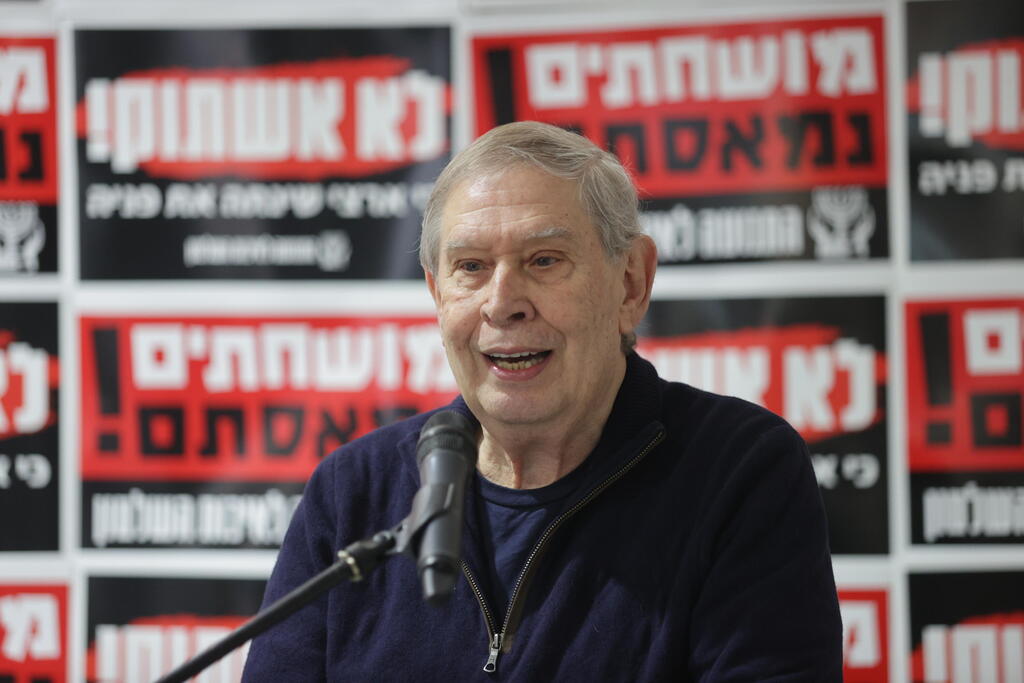
Former head of Israel’s Mossad intelligence agency Tamir Pardo told The Associated Press on Wednesday that Israel is enforcing an apartheid system in the West Bank, joining a small but growing list of retired officials to endorse an idea that remains largely on the fringes of Israeli political discourse and international diplomacy.
More stories:
Tamir Pardo becomes the latest former senior official to have concluded that Israel’s treatment of Palestinians in the West Bank amounts to apartheid, a reference to the system of racial separation in South Africa that ended in 1994.
Human rights organizations in Israel and abroad and Palestinians have accused Israel and its 56-year occupation of the West Bank of morphing into an apartheid system that they say gives Palestinians second-class status and is designed to maintain Jewish hegemony from the Jordan River to the Mediterranean Sea.
A handful of former Israeli leaders, diplomats and security personnel have warned that Israel risks becoming an apartheid state, but Pardo’s language was even more blunt.
“There is an apartheid state here,” Tamir Pardo said in an interview. “In a territory where two people are judged under two legal systems, that is an apartheid state.”
A senior official rejected Pardo's accusation calling it hyperbole and saying it bolsters Israel's enemies. "The use of the word apartheid by someone who was at the helm of one of Israel's security agencies is damaging and we will cost Israel in international litigations. It should not have been said," the official said.
The ruling Likud Party slammed Pardo for his comments. "We strongly condemn the shameful and dishonest claim," the Likud said in a statement, adding that Israel is acting more morally than any other nation when faced with a similar level of terrorism. "Jews, Arabs, Israelis and Palestinians alike are treated in Israeli hospitals, study and work together. Shame on you Pardo," the Likud statement read.
Given Pardo’s background, the comments carry special weight in security-centered Israel.
Pardo, who served as head of Israel’s clandestine spy agency from 2011-2016, wouldn’t say if he held the same beliefs while heading the Mossad. But he said that he believed among the country’s most pressing issues was the Palestinians — above Iran’s nuclear program, seen by Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu as an existential threat.
Pardo said that as Mossad chief, he repeatedly warned Netanyahu that he needed to decide what Israel’s borders were or risk the destruction of the Jewish state.
In the past year, Pardo has become an outspoken critic against Netanyahu and his government’s push to reshape the judicial system, slamming his old boss for steps he said would lead Israel to become a dictatorship. His candid evaluation Wednesday of Israel’s military occupation is rare among leaders of the grassroots protest movement against the judicial overhaul, which has generally avoided talk of the subject out of concern that it might scare away more nationalist supporters.
Pardo’s remarks, and the overhaul, come as Israel’s far-right government, which is made up of ultranationalist parties who support annexing the West Bank, is working to entrench Israel’s hold on the territory. Some ministers have pledged to double the number of settlers currently living in the West Bank, which stands at a half-million.
In apartheid South Africa, a system based on white supremacy and racial segregation was in place from 1948 until 1994. The rights groups have based their conclusions on Israel on international conventions like the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court. It defines apartheid as “an institutionalized regime of systematic oppression and domination by one racial group over any other racial group.”
Pardo said Israeli citizens can get into a car and drive wherever they want, excluding the blockaded Gaza Strip, but that Palestinians can’t drive everywhere. He said that his views on the system in the West Bank were “not extreme. It’s a fact.”
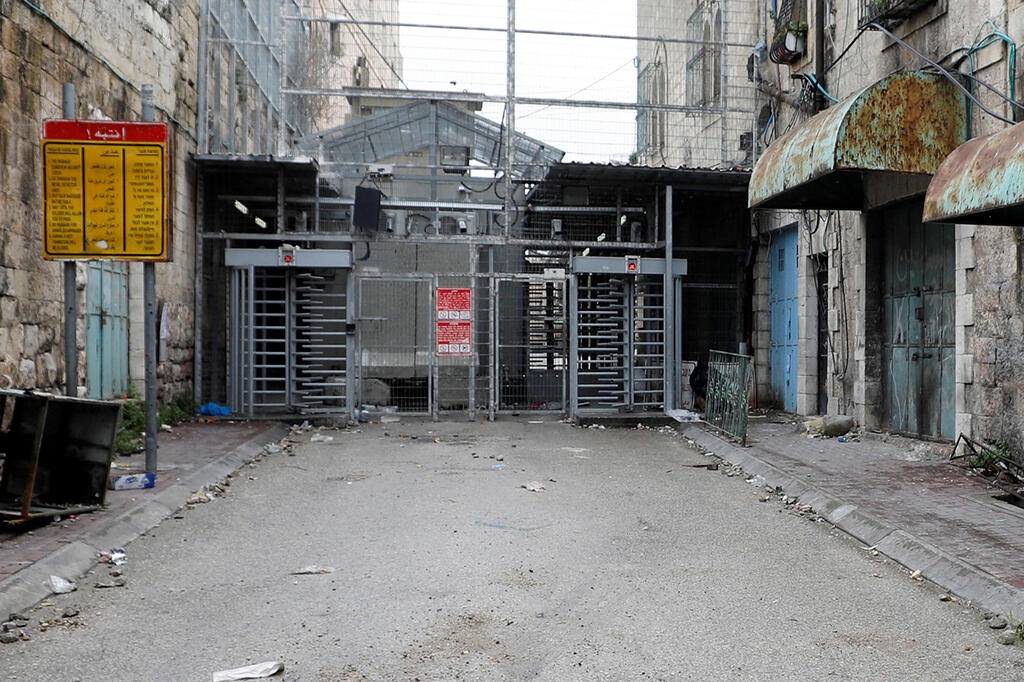
Israelis are barred from entering Palestinian areas of the West Bank, but can drive across Israel and throughout the 60% of the West Bank that Israel controls. Palestinians need permission from Israel to enter the country and often must pass through military checkpoints to move within the West Bank.
Rights groups point to discriminatory policies within Israel and in annexed east Jerusalem, Israel’s blockade of the Gaza Strip, which has been ruled by the Hamas terror organization since 2007, and its presence in the West Bank. Israel exerts overall control of the territory, maintains a two-tier legal system and is building and expanding Jewish settlements that most of the international community considers illegal.
Israel rejects any allegation of apartheid and says its own Arab citizens enjoy equal rights. Israel granted limited autonomy to the internationally recognized Palestinian Authority, which is based in the West Bank, at the height of the peace process in the 1990s and withdrew its soldiers and settlers from Gaza in 2005. It says the West Bank is disputed territory and that its fate should be determined in negotiations.
Pardo warned that if Israel doesn’t set borders between it and the Palestinians, Israel’s existence as a Jewish state will be in danger.
5 View gallery


IDF troops apprehend suspect in West Bank stabbing attack
(Photo: IDF Spokesperson's Unit)
Experts predict Arabs will outnumber Jews in Israel plus the areas it captured in 1967 — the West Bank, Gaza Strip and east Jerusalem. Continued presence could force Israel into a hard choice: Formalize Jewish minority rule over disenfranchised Palestinians — or give them the right to vote and potentially end the Zionist dream of a Jewish homeland.
“Israel needs to decide what it wants. A country that has no border has no boundaries,” Pardo said.