Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
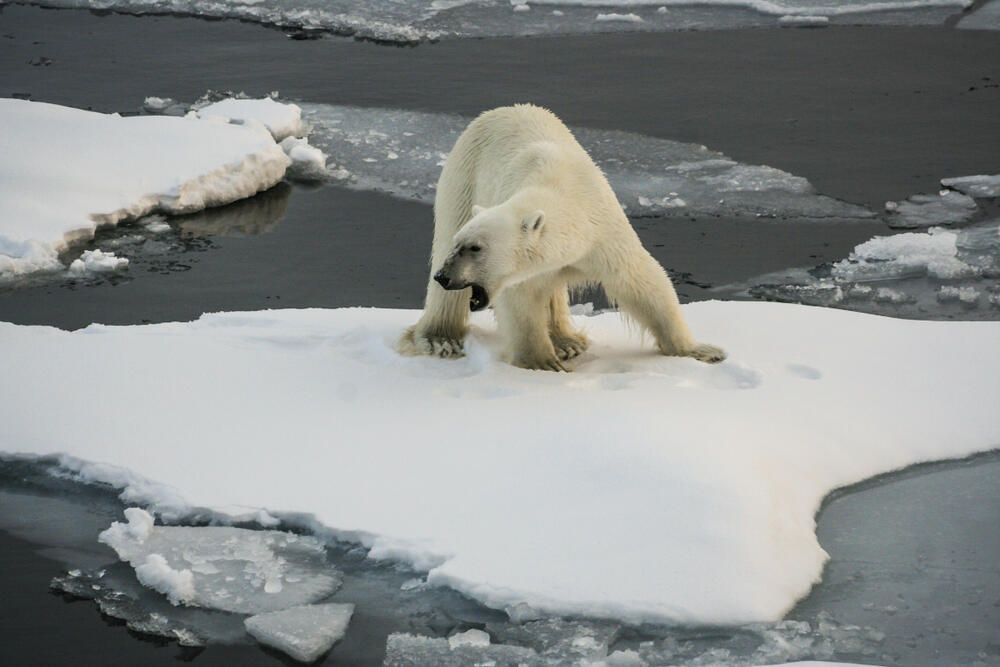
The southern and western subpopulations of polar bears in Canada's Hudson Bay are facing a significant threat of local extinction by the 2030s to mid-century due to climate change-induced thinning of sea ice and an extended ice-free period.
The loss of sea ice habitat, coupled with reduced hunting opportunities for seals (their primary food source), poses a critical challenge to polar bear reproduction and survival.
If global warming exceeds 1.5°C, polar bears in Western and Southern Hudson Bay will face serious threats, with the Western Hudson Bay projected to become unsuitable at around 2.2°C of warming, and Southern Hudson Bay no longer supporting bears at 1.6-2.1°C of warming.
The Hudson Bay region is unique as it thaws out entirely in summer, forcing bears to come ashore and fast while waiting for the ice to return.
The Western Hudson Bay population has already declined by 27% between 2016 and 2021, and by half since 1987.
This article was written in collaboration with Generative AI news company Alchemiq
Sources: newser.com, smithsonianmag.com, nytimes.com, abcnews.go.com, cbc.ca, nature.com, theaustralian.com.au, news.yahoo.com, natureworldnews.com, yahoo.com, wionews.com, newspressnow.com, ecowatch.com, theweathernetwork.com, winnipeg.citynews.ca, keyt.com, kion546.com, azocleantech.com, devdiscourse.com, wattsupwiththat.com.