Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
Israel has seen a record-breaking rise in sexually-transmitted diseases in recent months, despite the lockdown imposed to fight the spread of coronavirus.
There are growing concerns among medical professionals that an increasing number of STD-related bacteria have become resistant to antibiotics.
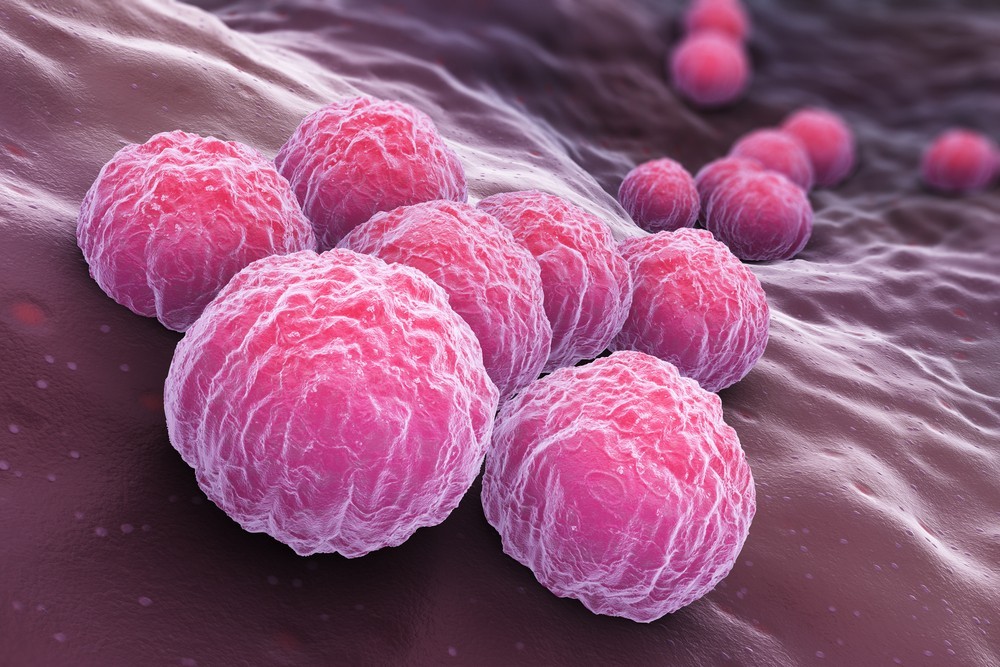
According to data collected by the Health Ministry, 860 cases of chlamydia and 314 cases of gonorrhea have been recorded since January 2020, a record number.
Israel saw 664 chlamydia infections and 254 diagnoses of gonorrhea for the first half of 2019.
The lockdown imposed to fight the spread of the virus was expected to lead to a drop in the number of STDs, but the opposite was found to have been the case, adding to global fears that extensive use of antibiotics has made bacteria more resistant to its effects.
The World Health Organization issued a warning earlier this year about the resistance of strains of bacteria that cause chlamydia, making it more difficult to treat as new forms of antibiotics quickly lose their effectiveness against the disease.
The bacteria that causes gonorrhea can infect both the genitals and the throat, and throat infections are often treated with the same antibiotics. This makes the area resistant to drugs used to fight gonorrhea, which is common in that part of the body due to oral sex.
Since the development of antibiotics, the bacteria has mutated and developed resistance to penicillin, Tetracycline and Quinolones due to overuse or incorrect dosages.
Chlamydia causes pelvic pain and inflammation, bleeding, pain during sexual intercourse, infections in the reproductive organs, and even sterility. But patients often do not present symptoms, causing infection in their sexual partners if a condom is not used.
Casual sexual relationships are a factor in the increased cases of STD, according to Dr. Bibiana Hazan, the head of the infectious diseases department at Emek Medical Center in Afula.
"When we ask patients why they have had unprotected sex, they often tell us that they believe condoms are for prevention of HIV and since that is no longer a fatal illness they are less vigilant. Others also say that they take PrEP [preventative medication] to protect themselves against HIV infection."
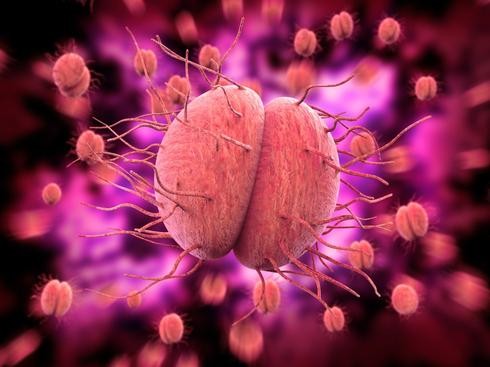
Gonorrhea is the more prevalent of the STDs, with 60 million people worldwide infected by it each year. The United States alone reports 3 million new infections annually.
, which causes the disease is also referred to as Gram-negative bacteria.
The name Gonorrhea comes from the ancient Greeks and means a discharge of semen. The ancient Greeks believed the discharge experienced by those infected, contained semen.
The bacteria that causes the disease, neisseria gonorrhoeae, is transmitted during sexual intercourse, but women can infect their babies during childbirth, causing conjunctivitis in newborns. Neonatal units in Israel and elsewhere in the West treat all newborn babies with antibiotic eye cream.
The disease can also be transmitted through objects that have been contaminated with the bacteria. Its gestation period can be anywhere from two days to two weeks but most often symptoms appear two to five days after contamination.
In 30% to 60% of women, no discernible symptoms would appear. The rest would experience vaginal discharge, pain while urinating, bleeding between menstrual cycles or after sexual intercourse. A clinical examination could show inflammation of the cervix and a discharge of pus.
Men with gonorrhea could have an inflammation of the urethra causing pain during urination and secretion of pus. In serious cases, the disease could inflame the pelvis causing stomach pain, bleeding, vomiting, and fever. The bacteria could also infect the testicles and the prostate gland.
Infection of the rectum would cause a discharge of pus, although rectal infections often present with no symptoms at all.