Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
We are used to thinking that bedbugs are common in Third World countries, but Europe, and especially France, recently faced an unprecedented infestation. French residents are suffering, the tourists are reluctant, and the municipality of Paris is having trouble finding a solution to the spread of the parasitic insects. So, what exactly does the bedbug do to humans, and what should anyone who travels in the City of Lights these days need to know.
Read more:
What is happening in France now?
The authorities there are dealing with an infestation of bedbugs. Most of the reports come from Paris, but there are also complaints from other cities. According to estimates, the bedbugs that attacked France have a very high breeding capacity, and are common not only in homes and hotel rooms, but also on seats in buses and the subway. In Paris, they fear that the bedbugs also will attack during the Olympics, which are supposed to be held there next summer, and the municipality has announced that it is starting to address the problem.
What is a bedbug?
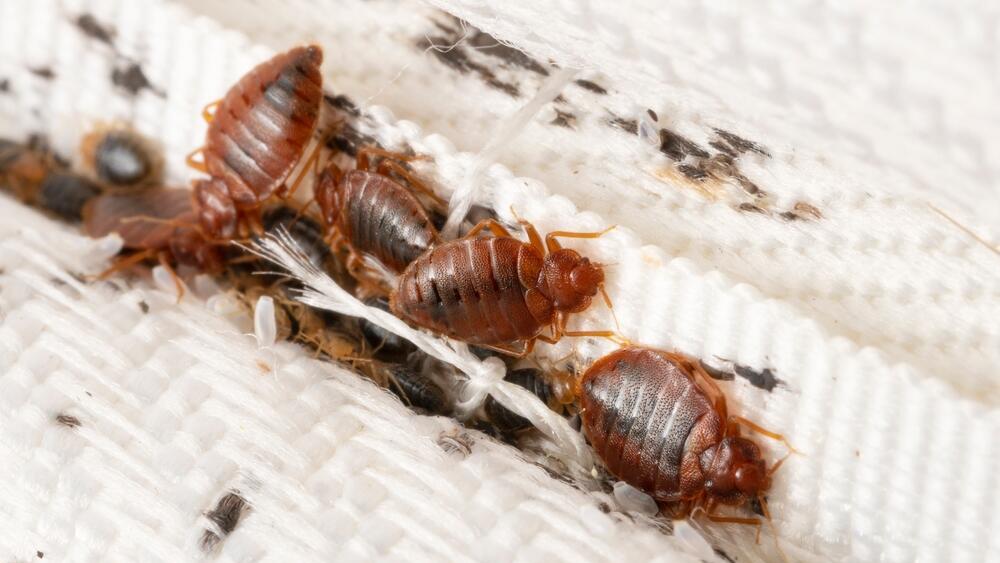
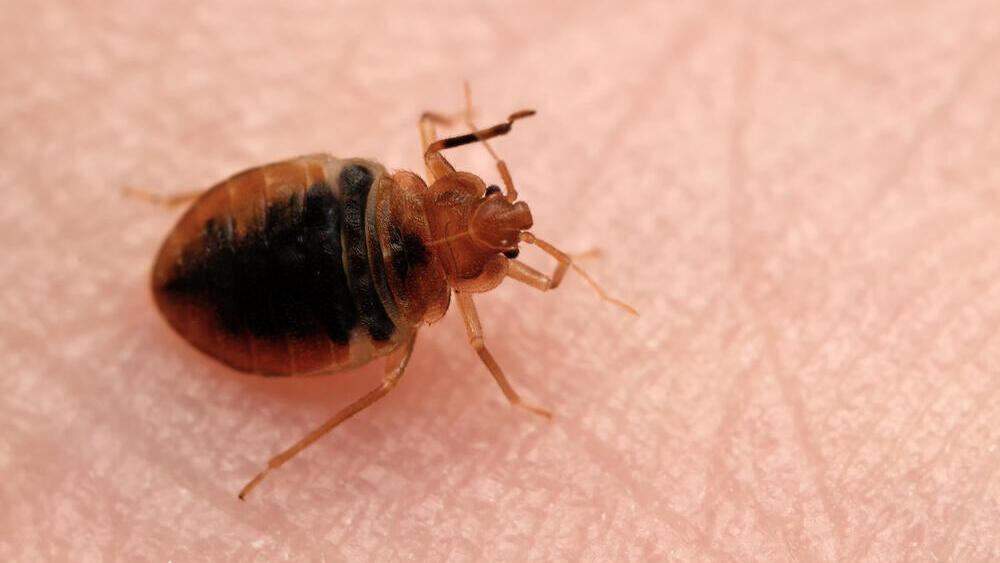
The bedbug (Cimex lectularius) is a small, flat parasitic insect that feeds exclusively on the blood of people and animals while they sleep. It is reddish-brown in color and wingless, its size is between one and seven millimeters, and it can live without a blood meal for as long as several months.
Bedbugs are found all over the world, even in five-star hotels and resorts, so their presence is not related to the cleanliness and living conditions where they are found.
Where are they located?
Bedbugs are found all over the world, from North and South America to Africa, Asia and Europe. Their presence has traditionally been seen as a problem in developing countries, but recently they have also reached the United States, Canada and Europe. Bedbugs have also been found in five-star hotels and resorts, so their presence is not related to cleanliness and living conditions where they are.
Under what conditions do they bite?
Their bites usually occur near areas where people sleep: apartments, shelters, residential buildings, hotels, cruise ships, buses, trains. During the day they hide in different places such as mattress seams, springs, bed frames, headboards, dressers, cracks, crevices and behind wallpaper. Bedbugs have been shown to be able to bite at night even at a height of 30 meters, but tend to live within two meters of where people sleep.
Do bedbugs spread diseases?
No, but it is a nuisance because the bite causes itching, which can lead to scratching and infection.
Is the bite itself dangerous?
The bite of the bedbug - which is, in fact, a biting and sucking of the skin - affects each person differently. The bite reactions can range from no physical signs at all, to a small bite mark, to a severe allergic reaction. The bedbug is not considered dangerous, but some people have a significant allergic reaction after a few bites, and this will require medical treatment, whether with an anti-allergic or corticosteroid ointment or oral antihistamines.
What are the signs and symptoms of a bedbug bite?
One of the easiest ways to identify bedbug infestations is to discover bite marks on the face, neck, arms, hands or any other part of the body. The signs can also appear two weeks after the bite, so the way to know if there are bed bugs in your environment is by finding their remains in the folds of the mattress and sheets, in rusty blood stains that the bedbugs secrete on the mattress or on nearby furniture, or by a sweet musty smell that indicates the presence of their secretions.
Bedbug bites are not usually a serious medical problem. The best way to treat it is to avoid scratching the area, and to apply an ointment. In more severe cases, the doctor will recommend taking oral antihistamines.
How do you know you've been bitten?
It is difficult to tell if you have been bitten by a bedbug, unless you find bedbugs or signs of infestation. When bed bugs bite, they inject an anesthetic and anticoagulant that prevents a person from knowing they have been bitten. Most people don't realize they've been bitten until bite marks appear, which can happen several days after the bite. The signs are similar to mosquito or flea bites - a slightly swollen and red area that may itch and irritate. The bite marks may be random or appear in a straight line. The bites can cause sleep problems, anxiety and skin problems resulting from excessive scratching.
Who is at increased risk of being bitten?
Everyone. As far as is known, bedbugs do not distinguish between humans.
How do you treat bites and prevent the presence of bedbugs?
Bed bug bites are not usually a serious medical problem. The best way to treat it is to avoid scratching the area, and to apply an antihistamine or corticosteroid ointment. In more severe cases, the doctor will recommend taking oral antihistamines. Bed bug extermination is carried out by means of spraying by a professional.