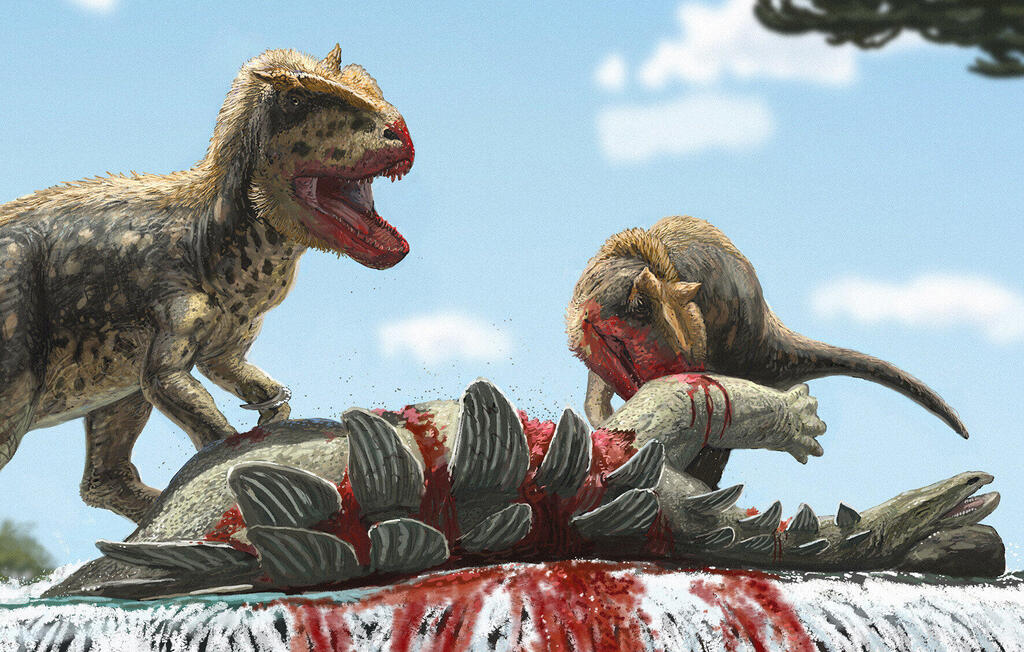
Theropod dinosaurs are among the most fascinating and significant groups in the dinosaur kingdom, including iconic predators like Tyrannosaurus and Allosaurus, as well as their modern descendants, birds. Just as lions today roam the African savannas and tigers prowl the Asian forests, creatures like Allosaurus dominated North America and Southwestern Europe during the Jurassic period, while Metriacanthosaurus, another formidable predator, stalked the lands of China. Until recently, the vast area stretching from Central Europe to East Asia was a "terra incognita" – a mysterious, uncharted land in terms of large Jurassic predators.
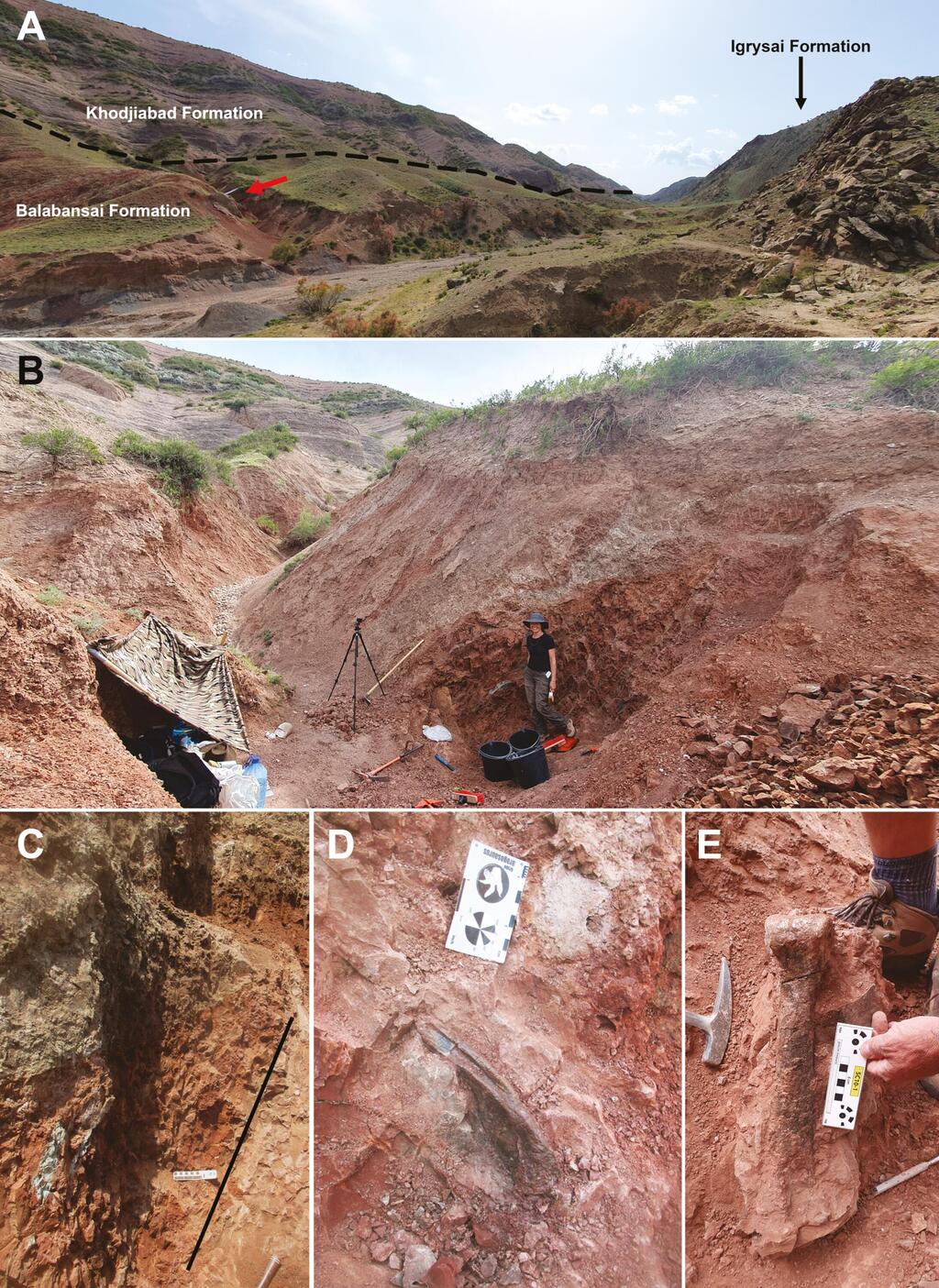
That was until a game-changing discovery turned everything on its head. The remains of a dinosaur named Alpkarakush kyrgyzicus were unearthed in Kyrgyzstan, marking the first-ever find of a theropod dinosaur in the region. This incredible milestone was achieved by Kyrgyz paleontologist Dr. Isaak Bakirov, who uncovered these remains near Tashkumyr in the western part of the country in 2006. These fossils date back approximately 165 million years.
This discovery sparked a series of excavations that have since revealed a treasure trove of fossils, including skull fragments, vertebrae, pelvic bones and limb bones. Careful analysis of these finds has led to the conclusion that this was a predatory dinosaur stretching an impressive 10 yards in length.
4 View gallery
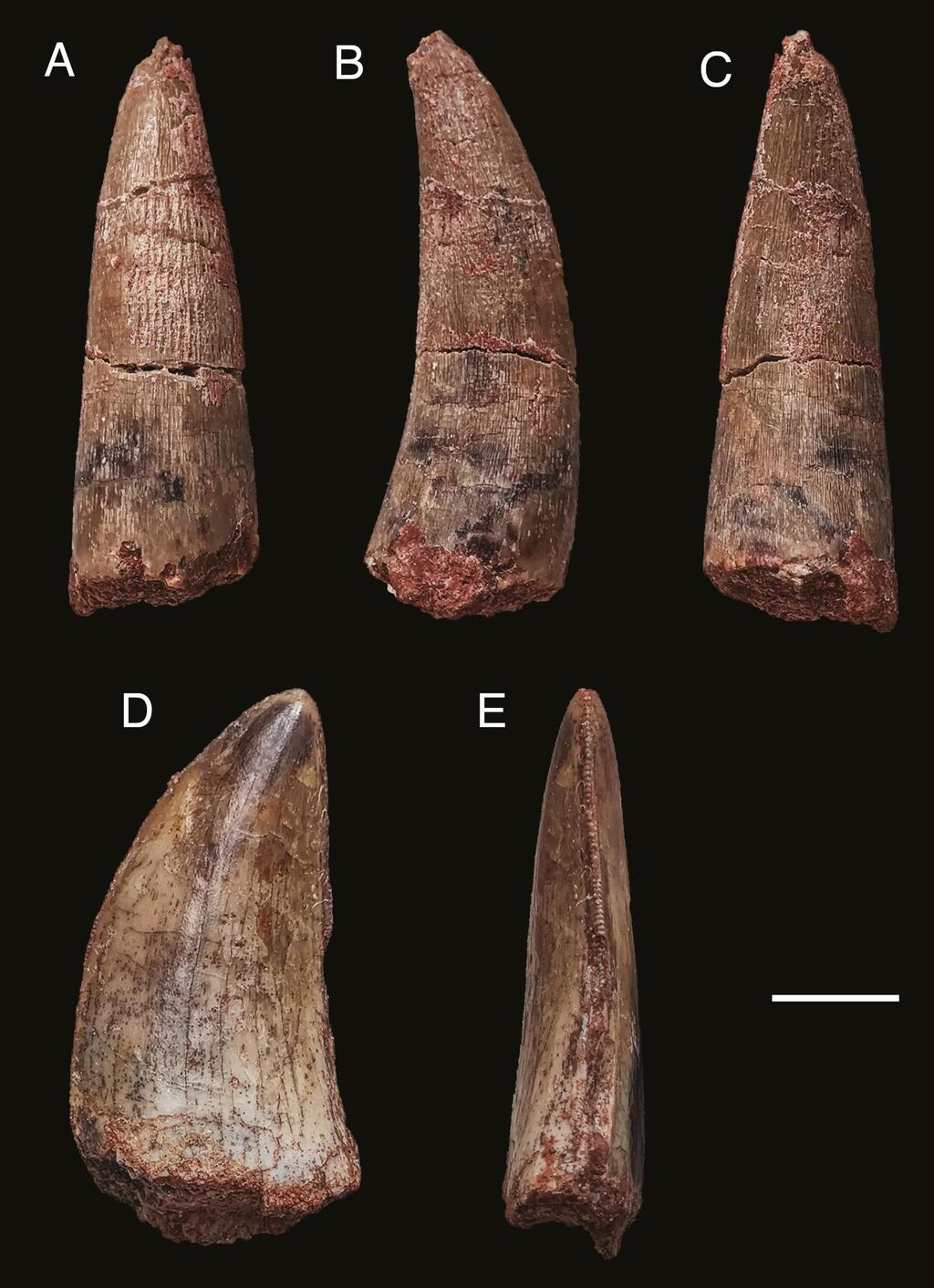


Fangs of the Alpkarakush kyrgyzicus
(Photo: Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society)
What's even more exciting is that this newly identified species boasts features never seen before. One standout feature is a prominent "brow" on a skull bone (postorbital), suggesting the presence of a horn. Additional unique characteristics, detailed in the Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, were identified in the dinosaur's vertebrae and femur.
Comparisons with other theropods suggest that this new species is part of the Metriacanthosauridae family, closely related to the great predatory dinosaurs of East Asia. It's believed that the Metriacanthosauridae and other key theropod groups originated in Southeast Asia, spreading across continents via Central Asia and Europe. "This discovery fills a massive gap in our understanding of Jurassic theropods and offers thrilling new insights into their evolution and biogeography," says Professor Oliver Rauhut from the Bavarian State Collection for Paleontology and Geology in Munich, part of the research team.
4 View gallery
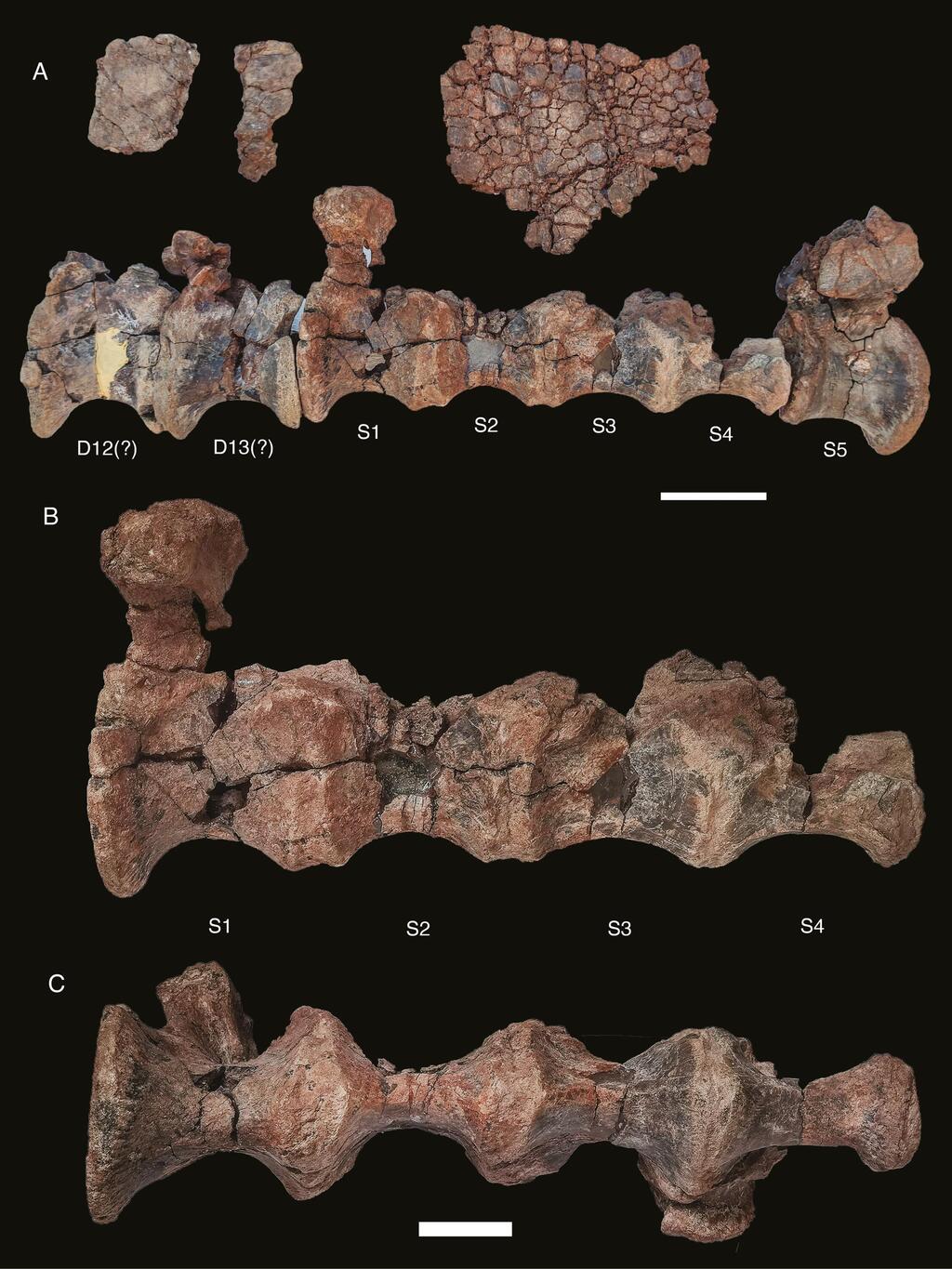


Vertebrae of Alpkarakush kyrgyzicus
(Photo: Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society)
At the excavation site where the remains were uncovered, additional, slightly smaller specimens of Alpkarakush kyrgyzicus were found. A detailed examination of the bone's internal structure revealed the larger specimen belonged to a dinosaur that had nearly reached full maturity of at least 17 years old, while the smaller one was at an intermediate stage of maturity. Researchers have hypothesized that these two might represent a parent and its offspring that roamed together around 165 million years ago.
"3D models of the bones from this predatory dinosaur have been created and are now accessible online, enabling researchers worldwide to conduct further studies and produce 3D prints," according to Dr. Oliver Wings, director of the Natural History Museum in Bamberg.
The fossil is named after Alpkarakush, a giant bird from the traditional Kyrgyz epic "Manas," which unites the Kyrgyz tribes and often aids heroes at crucial moments. The second part of the predatory dinosaur's name directly references the Kyrgyz Republic, since its bones were discovered on its soil.
There is now a drive to secure sufficient funding to support the reconstruction of this dinosaur's skeleton, which is anticipated to be the first of its kind displayed in Kyrgyzstan at the National History Museum in the capital of Bishkek, the largest city in the central Asian Republic.