The discourse on egg freezing has developed significantly in recent years. The average age at which women want to become pregnant is increasing in the Western world; at the same time, social isolation during the period of the coronavirus pandemic served as a reminder of the fact that pregnancy cannot be postponed indefinitely - The biological clock is ticking.
Read more:
What does someone who has reached the age of 35 and still hasn't found the time, or is currently focused on a career, do? You should consider undergoing a process of fertility preservation.
The treatment is currently provided in the health services basket for certain conditions, and not only in the case of cancer, which also allows young women to undergo it.
What exactly is the process of egg freezing, who is it for and under what circumstances? I will try to present here all the relevant questions and answer them.
What is egg freezing (fertility preservation)?
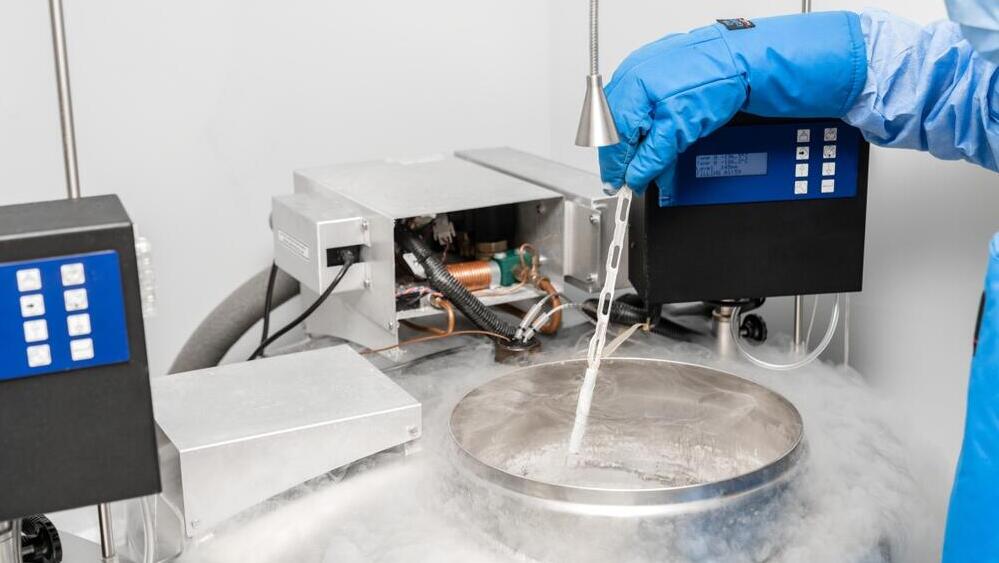
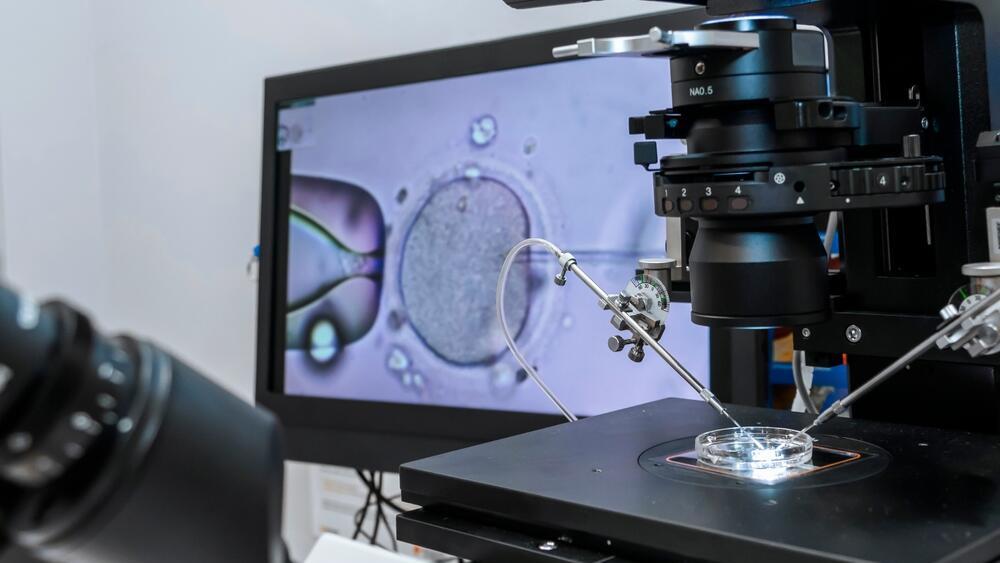
This is a procedure designed to preserve the potential for future pregnancy, in which the eggs that develop in a specific month in the ovary are extracted, after hormonal stimulation. The eggs can be frozen without fertilization or after fertilization with sperm and growth of the fertilized eggs for several days in the laboratory - that is, embryo freezing.
In the past, fertility preservation was allowed only for women with malignant diseases or diseases whose treatment required chemotherapy treatments, because the drugs for these diseases have a high potential to damage the ovaries. In recent years, fertility preservation has been approved for non-medical reasons – that is, "preservation by choice" for the purpose of postponing parenthood.
Conservation for medical reasons will also be offered to women at increased risk due to amenorrhea That is because even if the woman is young and of reproductive age, the number of potential eggs in her ovaries is lower compared to other women her age, which may create future fertility problems as the woman postpones the age of becoming pregnant.
Who should undergo egg freezing?
Many women applied to have the procedure done during the period of the coronavirus pandemic, and it was found that they had a poor ovarian reserve, so that very few eggs were recovered with each harvesting, even though the hormonal treatment was at the maximum. This may indicate an increased risk due to amenorrhoea or early menopause. It is important to raise awareness of the issue among young women as well, as their childbearing age may be lower than expected. Many efforts are being made to raise awareness among gynecologists and family doctors, to encourage women of childbearing age to contact a fertility clinic, to find out the status of their ovarian function and to undergo fertility preservation if the ovary reserve is poor.
If there is no medical problem, why undergo egg freezing?
The question is legitimate, and it comes up more than once in meetings with patients. The explanation is very logical. From the moment we are born, the number of eggs in the ovary decreases, with the rate of decrease being more significant after the age of 35. In many cases, only when women try to conceive do they discover that there is a problem, because menstrual cycles remain regular and normal even when there is a decrease in ovarian function.
The average age at which a woman has her first child has been increasing all over the world in recent years, for various reasons, but with all the existing technologies and laboratory capabilities, there are still many things beyond our control. Fertility preservation can prevent much heartache in the future.
At what age can egg freezing be done?
The start of treatment for egg freezing depends on medical indication, that is, according to the problem and the level of ovarian function. Eggs can be frozen for patients ages 30 to 41
What are the situations that allow or require fertility preservation?
Women who require treatments with a risk of ovarian damage, such as chemotherapy or radiation to the pelvis, can perform fertility preservation until the age of 41 at the expense of the health services basket. The goal is to perform the egg extraction before starting the treatments. In these cases, another option – preserving pieces of the ovary – can be considered.
Another situation is conservation by choice for women who are not interested in children at this stage and prefer to postpone parenthood.
Preservation for medical reasons is given to women up to the age of 39 who have an increased risk of early menopause, according to the following conditions:
- Women with signs indicating poor ovarian reserve.
- Women who must undergo surgery to remove both of their ovaries.
- Women with genetic or other diseases related to a decrease in ovarian reserve at a young age (chromosomal or autoimmune syndromes).
It is recommended for every woman of childbearing age to consult a doctor and check their ovarian reserve. Ovarian reserve is a condition that cannot be changed, but something can definitely be done about it, if you start early.
How many eggs do I have? The criteria by which the ovarian reserve is determined
The tests to be performed: hormonal profile during menstruation for FSH level, AMH test (hormone secreted by the ovary) and ultrasound test to count the follicles in the ovary. If two of these three indicators are low according to the established criteria, the situation will be defined as a low reserve and will entitle the woman to treatments at the expense of the health basket. For women with normal ovarian reserve who do not plan to give birth in the near future, it is recommended to perform egg preservation for a fee.
How is the egg freezing process performed?
The fertility preservation method varies and can be egg preservation or fertilized egg preservation. The treatment includes injecting hormones similar to those secreted by the brain, FSH and LH, and monitoring the development of the follicles with blood tests and ultrasound once every three to five days. When the follicles reach a size of 17-18 mm, the woman will receive another injection, the purpose of which is to start the process of maturing the eggs for harvesting.
3 View gallery
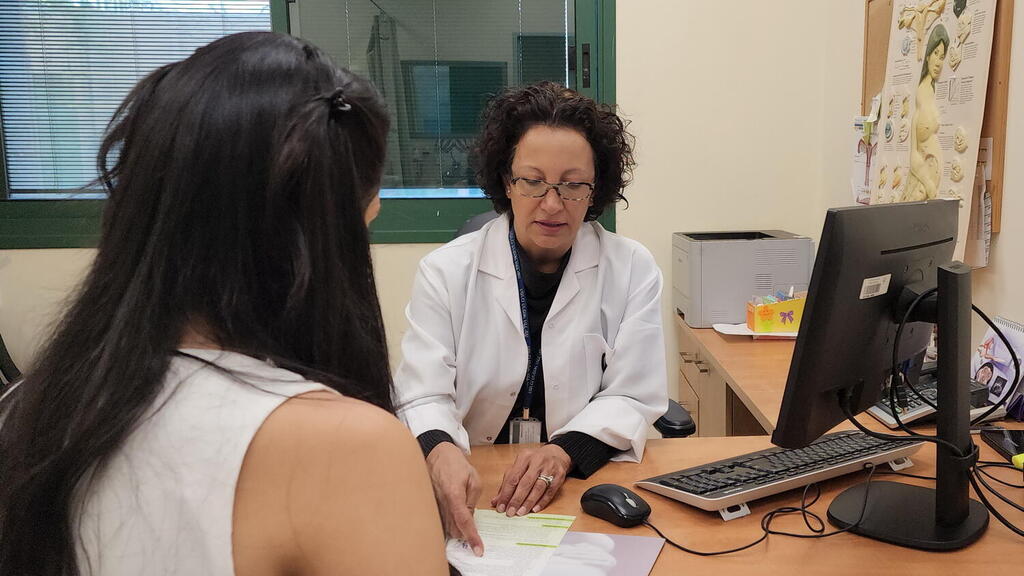


Counseling meeting before fertility preservation with Prof. Einat Shalom-Paz
(Photo: Hillel Yaffe Spokesperson)
The ovarian stimulation protocol is determined by the attending physician according to the number of follicles in the ovary and with the goal of obtaining the maximum number of eggs without endangering the woman.
The woman is hospitalized on the day of the egg retrieval. The suction operation is performed under general anesthesia in an operating room. A fluid infusion will be connected into the vein. The follicles are harvested using a normal vaginal ultrasound transducer. A needle is attached to it that pierces the follicle in the ovary through the vagina and draws the fluid inside, including the egg, into a special test tube. The test tube is transferred to the laboratory, where the eggs are isolated from the follicular fluid, and they are transferred to flasks containing tissue culture fluid. After a short incubation period, the eggs are frozen for future use.
After the harvesting, the woman stays in the recovery room and then in the women's department for about two to four hours and is discharged home depending on her condition.
How many treatment cycles are performed?
The treatment includes up to six cycles or until obtaining 25-30 eggs (whichever comes first). Women who have undergone fertility preservation procedures in the past will be able to perform another round, according to their desire and their age at the time of the previous harvesting. Fragile X pre-mutation carriers will undergo up to six cycles of treatment or until 40 eggs are obtained (whichever comes first) due to the need to perform preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) and a statistical risk of half of the eggs being abnormal.
The treatment will be given for the birth of a first and second child to spouses who do not have children in their current marriage, as well as to a single woman, young woman or girl who does not have children, for the purpose of preserving fertility. For these women, the ovarian tissue will be preserved,and an implant is also included in the basket.
The eggs will be frozen free of charge until the birth of two children or until the woman turns 42. If indicators of a low reserve are found, it will be possible to finance the treatment and harvestn g and subsidize the cost of the drugs.
Professor Einat Shalom-Paz is the director of the in vitro fertilization unit at the Hillel Yaffe Medical Center in Hadera.