Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
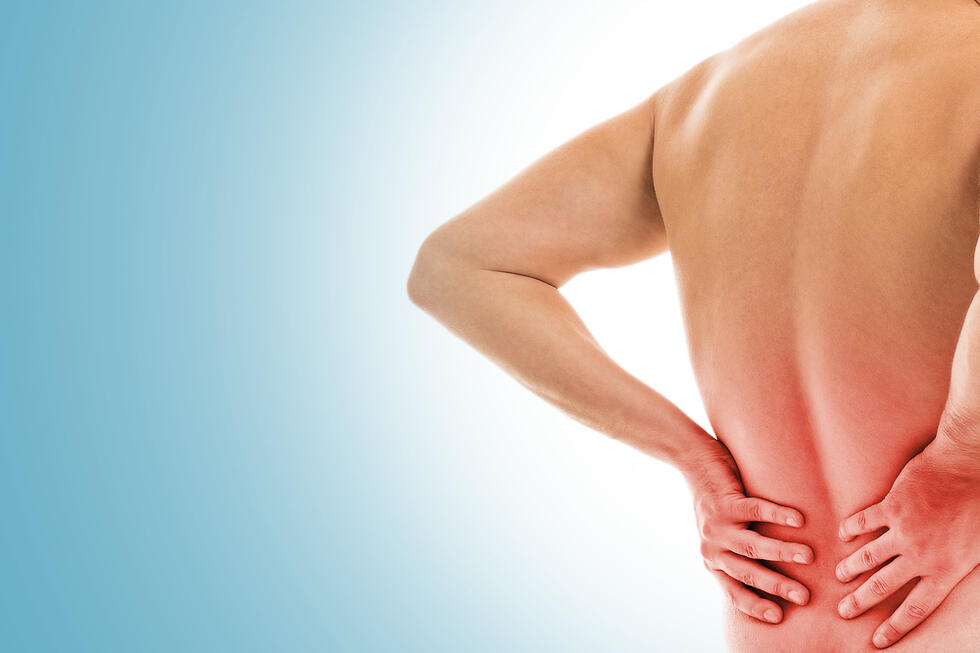
A recent study published in the British journal BMJ Open revealed that reducing daily sitting time can prevent the worsening of back pain. The study involved 64 middle-aged participants who were overweight or obese and spent most of the day sitting. These factors increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases and back pain.
Doctoral researcher and physiotherapist Jooa Norha from the University of Turku, who was involved in the study, stated, "Our participants were fairly normal middle-aged adults who spent a lot of time sitting, exercised little, and had gained some extra weight. These factors not only increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases but also of back pain." Participants were divided into two groups: half were asked to reduce their daily sitting time by one hour and incorporate light exercises into their routine, while the other half maintained their usual routine.
Over six months, the researchers monitored the participants' sedentary behavior and physical activity using an app connected to an accelerometer. They also utilized magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and positron emission tomography (PET) based on a radioactive tracer to measure back musculature. This approach allowed them to examine the possible mechanisms for preventing back pain.
The findings showed that participants who reduced sitting time by an average of 40 minutes a day and engaged in light to moderate physical activity exhibited stable back pain levels, while the inactive group experienced a sharp increase in pain intensity. Finnish researchers discovered that when people with back pain sat even a little less each day, their pain was less likely to progress over the next six months.
"We did not observe that changes in back pain were related to modifications in fat or glucose metabolism in the back muscles," Jooa Norha clarified. This indicates that back pain can be prevented or alleviated even without improvements in muscle composition or metabolism. The study did not find a relationship between discomfort and these improvements, suggesting that other mechanisms might underlie the therapeutic effect.
The results reinforce the current understanding of the relationship between activity and back pain, although the exact mechanisms by which increased activity alleviates back pain remain unclear. "Just how being more active curbs back pain isn't clear," acknowledged Norha. Previous results from the same research group and others suggest that sitting may be harmful to back health, but the data is preliminary.
Back pain is a condition suffered by millions of people worldwide and limits daily activities. According to recent analysis published in the journal Lancet Rheumatology more than 800 million people will suffer from lower back pain by 2050, a 36 percent increase from 2020. In 2020, there were approximately 619 million cases of back pain.
Some people are more prone to back pain due to excessive fat deposits in the back muscles, and poor glucose metabolism or insulin sensitivity may predispose them to pain. Lack of movement causes back muscles to weaken, reducing their ability to support body weight and maintain good posture. Switching between postures is more important than only looking for the perfect posture, as it can help alleviate back pain.
The researchers confirmed that standing and reducing sitting periods are particularly beneficial for people who are overweight and less physically active. However, physical activity, such as walking or more vigorous exercise, is better than just standing.
Norha recommends that people "reduce the time they spend sitting at work or during their leisure time," noting that physical activity is essential for back health.
Regular physical activity, even in small doses, can protect against back pain and significantly reduce the risk of developing back pain. If you are prone to back pain or excessive sitting, try to reduce your sitting time and add light exercises like walking or brisk activities to your daily routine. The recommendation to lose fat in the back and avoid pain in this area is to engage in physical activities, such as walking or doing more intense exercises.
The study serves as a wake-up call to the necessity of doing light exercises and reducing sitting time to avoid chronic back pain and other health issues. Finnish researchers found that reducing periods of inactivity, such as sitting for long periods, can help prevent the worsening of chronic back pain, as participants who sat less each day experienced less pain progression.
Overall, this study strengthens the argument for incorporating more physical activity into daily routines as a strategy for managing back pain. Back pain can be prevented or alleviated even without improvements in muscle composition or metabolism. The findings highlight the importance of reducing periods of inactivity to significantly help in treating back pain.
This article was written in collaboration with Generative AI news company Alchemiq
Sources: ScienceDaily, Zee News, La Razón, La Voz, elEconomista.es, Diario EL PAIS Uruguay, La Nacion, O Globo