Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
Fifty years ago, the Jordanian army launched a huge offensive that went down in history as "Black September" in a bid to retake control of territory occupied by the Palestine Liberation Organization in Jordan.
Here is an account of the bloody confrontation on September 17, 1970, based on AFP's copy at the time.
4 View gallery
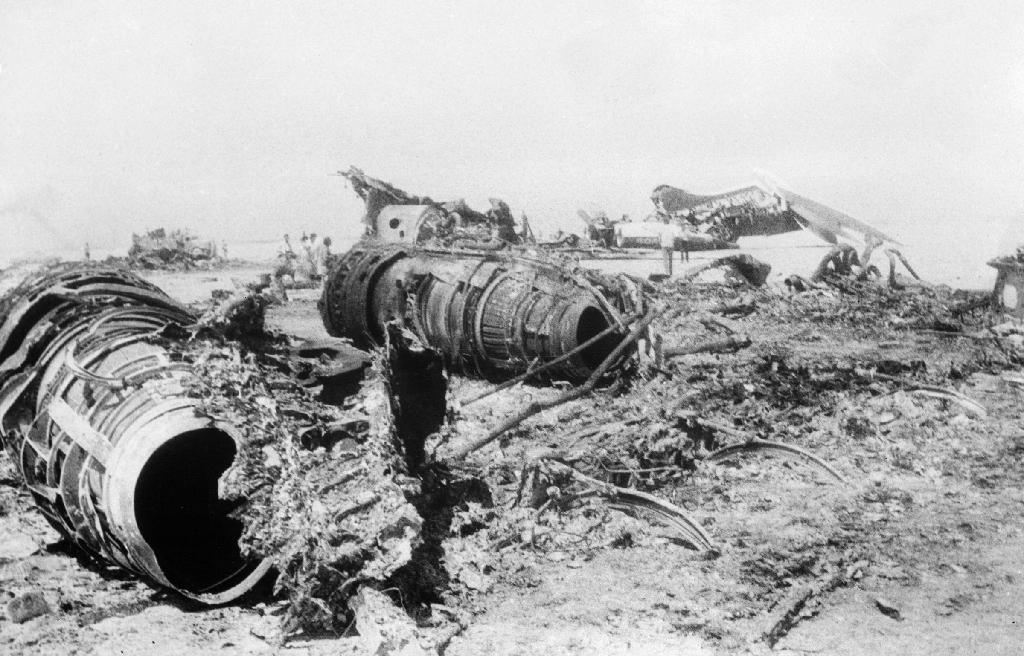


This file photograph taken on September 7, 1970, shows wreckage of the Swissair, TWA and BOAC aircraft in Zarka (Dawson's Field) in the Jordanian desert, which were hijacked September 6 and 9 1970 by The Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine (PFLP), leading to the events of 'Black September'
(Photo: AFP)
The Arab defeat in the 1967 Six-Day War in which Israel seized the West Bank and other land, resulted in the Palestinian resistance becoming more radical.
Yasser Arafat, who became PLO chief in 1969, set up training camps and military bases for his 40,000-strong army of fedayeen guerrillas in Jordan, to attack the neighbouring Jewish state.
Jordan had taken in hundreds of thousands of Palestinian refugees since the creation of Israel in 1948.
But the power of the Palestinian armed groups developed into a state within a state.
4 View gallery
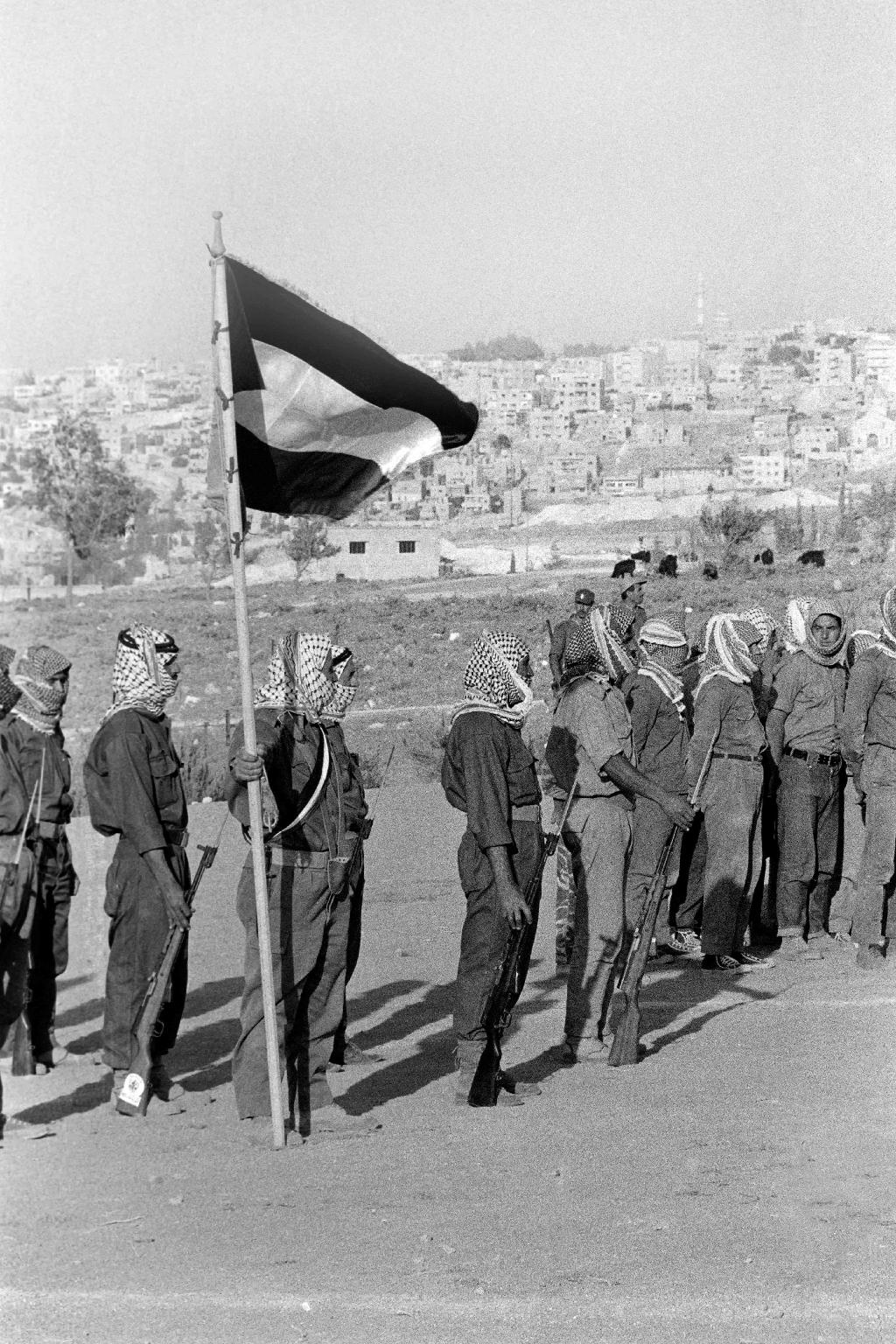


In this file photograph taken on August 17, 1970, militiamen of El Fatah Palestinian resistance movement, parade in Amman, Jordan, at the end of a training session chaired by Yasser Arafat, President of the Central Committee of the Palestinian National Council
(Photo: AFP)
Insecurity set in and shoot-outs became commonplace in the streets of Amman. King Hussein of Jordan, who struggled to control factions of his own army, narrowly survived a number of assassination attempts.
In mid-1970, Egypt and Jordan accepted a U.S. plan, based on UN Security Council Resolution 242, which involved recognition of the state of Israel. The Palestinians rejected it.
Fierce crackdown
In early September 1970, the leftist Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine (PFLP), a Marxist faction led by George Habash, hijacked five planes, forcing three to land in the Jordan desert.
It blew them up once they had been emptied of several hundred passengers, taking dozens hostage.
On September 17 a deeply frustrated King Hussein responded by ordering his 50,000-strong army to kick the Palestinian fighters out of the Hashemite kingdom.
Tank divisions, their faces blackened with soot, pushed into the centre of Amman, refugee camps on the outskirts of the capital and Palestinian training centres.
4 View gallery
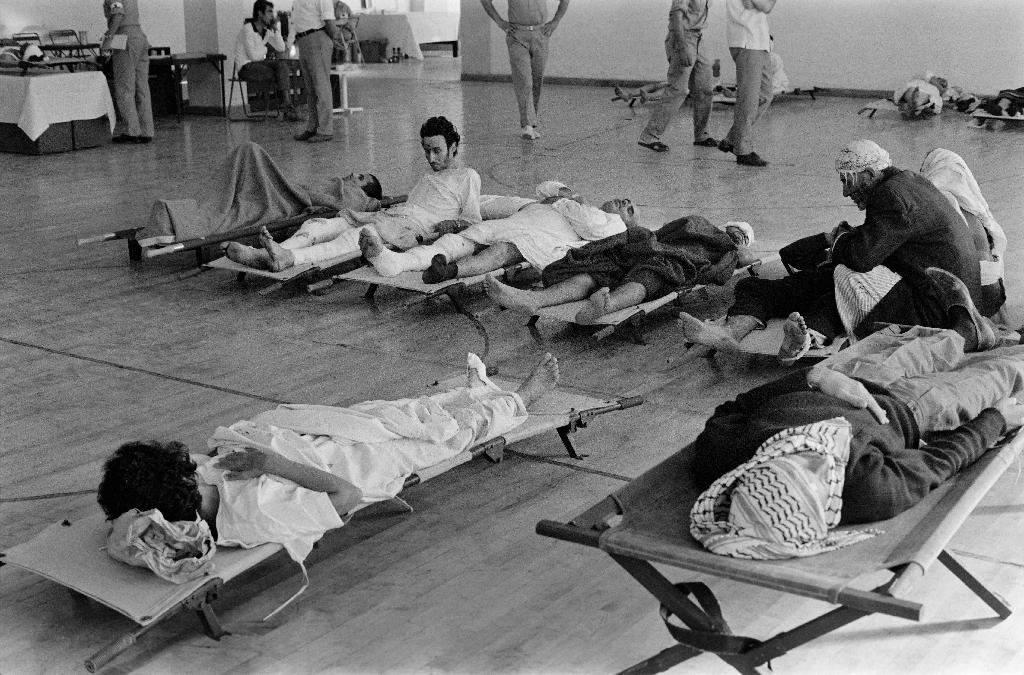


In this file photo taken on October 02, 1970 Wounded Palestinians coming from the Palestinian refugee camp of Wihdat wait at the French field hospital in Amman, on October 02, 1970
(Photo: AFP)
The next day clashes extended to Irbid, Zarka and al-Ramtha in northern Jordan, which were pounded with heavy artillery by Jordanian troops. On September 20, Syria intervened to back the Palestinians, sending armoured vehicles into northern Jordan, forcing the Jordanian army to fight on two fronts.
Journalists who had been stranded in their hotel overlooking Amman emerged three days later to a battle-scarred capital. "No neighbourhood has been spared. All the houses show traces of the fighting, some have been gutted by a shell, others hit by volleys of heavy weapons fire," AFP's journalists wrote.
"The Palestinian Wahdat camp in Amman, the PFLP's stronghold, is just a pile of smoking rubble," they added.
In the fighting, 3,000 Palestinian fighters, Jordanian soldiers and civilians were killed according to Jordan, while the PLO puts the toll in the tens of thousands.
Palestinians expelled
On September 27, after 10 days of bloody fighting, a ceasefire was signed in Cairo.
The last hostages held by the PFLP were freed two days later.
But under the deal the Palestinian armed groups got to stay in Jordan, and new fighting took place in January and March 1971.
4 View gallery
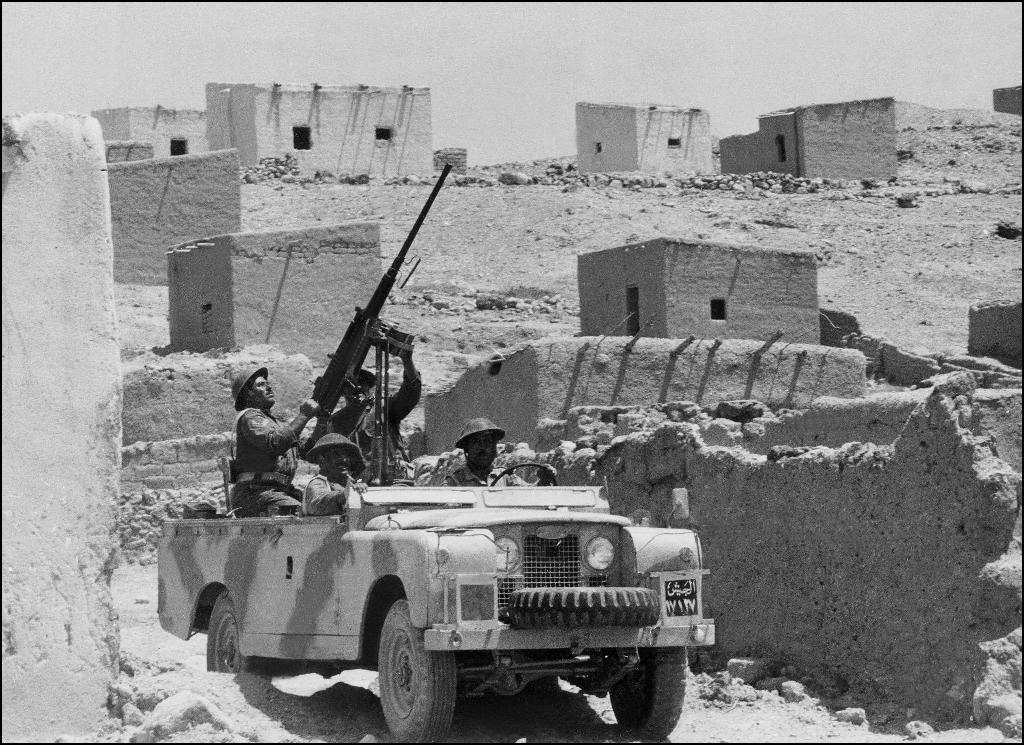


In this file photograph taken on October 29, 1970, Jordanian soldiers patrol in an armed jeep in the Jordan valley
(Photo: AFP)
Prime Minister Wasfi al-Tel eventually drove Arafat and the Palestinian fighters out in July 1971, forcing them to seek safe haven in Lebanon.
"It was inevitable, because it was either them or us," King Hussein later said.
In the 1980s Arafat and King Hussein reconciled, but their relationship remained tinged with suspicion.
'Black September' organization
On November 28, 1971, Tel, regarded as King Hussein's confidant, was assassinated in Cairo by members of the new radical Palestinian "Black September" organization.
The group would go on to claim numerous attacks, the most spectacular of which was the hostage-taking of Israeli athletes at the 1972 Munich Olympics.
On September 5, 1972, eight gunmen broke into the Israeli team's flat at the Olympic village, shooting dead two and taking nine more Israelis hostage, threatening to kill them all unless 232 Palestinian prisoners were released.
West German police responded with a bungled rescue operation in which all nine hostages were killed, along with five of the eight hostage-takers and a police officer.