Israeli archaeologists on Monday said they have unearthed a massive ancient winemaking complex dating back some 1,500 years.
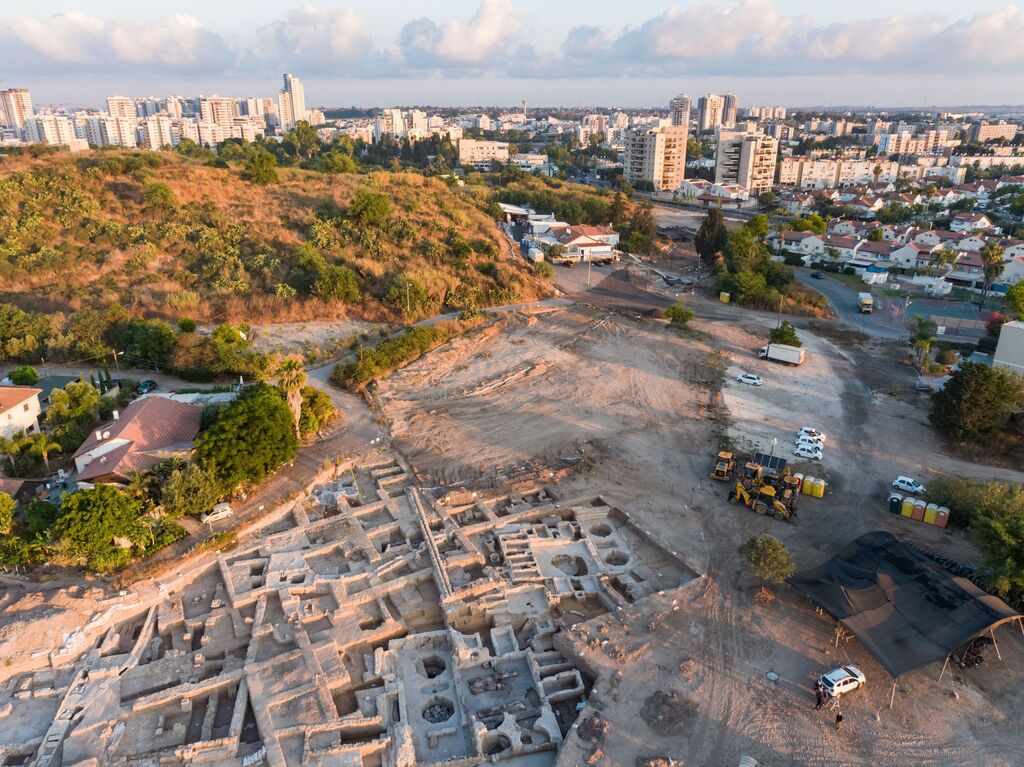
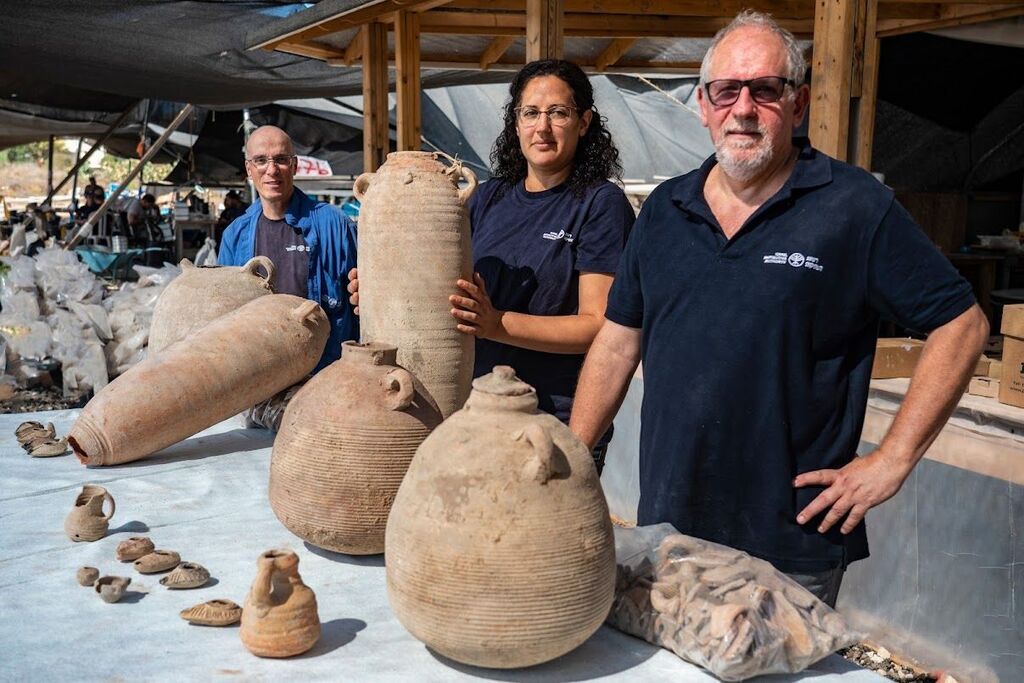
The complex, discovered in the central town of Yavne, includes five wine presses, warehouses, kilns for producing clay storage vessels and tens of thousands of fragments and jars, they said.
Israel’s Antiquities Authority said the discovery shows that Yavne was a wine-making powerhouse during the Byzantine period. Researchers estimate the facility could produce some 2 million liters (over 520,000 gallons) of wine a year.
Jon Seligman, one of the directors of the excavation, said the wine made in the area was known as “Gaza” wine and exported across the region. The researchers believe the Yavne location was the main production facility for the label.
“This was a prestige wine, a light white wine, and it was taken to many, many countries around the Mediterranean,” he said, including Egypt, Turkey, Greece and possibly southern Italy.
Seligman said wine was not just an important export and source of enjoyment in ancient times. “Beyond that, this was a major source of nutrition and this was a safe drink because the water was often contaminated, so they could drink wine safely,” he said.
The antiquities authority said the complex was uncovered over the past two years during excavations being conducted as part of the development of Yavne, a town located south of Tel Aviv.